Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2018-07
-
br FXR FGF in the control of
2022-03-30
FXR–FGF15/19 in the control of BAs synthesis The nuclear receptor FXR is the master regulator of BAs homeostasis, modulating their synthesis, GANT61 and uptake [15]. FXR decreases BA de novo hepatic biosynthesis by reducing the expression of CYP7A1. At the canalicular membrane, newly-synthesized
-
Emerging evidence has shown that
2022-03-30
Emerging evidence has shown that pharmacological FXR agonism attenuates chronic alcohol treatment-induced liver injury and steatosis [18], [19], while whole-body FXR knockout worsens alcohol-induced liver injury [19]. This suggests that FXR plays an important role in ALD development. However, defici
-
The diverse biochemistry of zinc
2022-03-30
The diverse biochemistry of zinc means that, in many cases, more than one factor (or pathway) is at play. Whilst catalytic Zn2+ sites are now typically well-understood, the recognition that Zn2+ levels regulate the function of many cell types has led to vigorous interest in the fate and role of mobi
-
In addition to removing proteins and organelles
2022-03-30
In addition to removing proteins and organelles related to iron and lipid metabolism, an alternative mechanism by which autophagy promotes ferroptosis is through the formation of the BECN1-solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) complex [42,43]. SLC7A11 is the main component of the antiporter sy
-
Aberrant activity of PRC as a result of over
2022-03-30
Aberrant activity of PRC2 as a result of over expressed EZH2, has been frequently seen in a wide range of human cancers including breast and prostate tumors [10]. However, leukemia-associated epigenetic aberrations are not fully understood [7]. Herein, we will overview the current knowledge of epige
-
dormin sale We reveal that the four well
2022-03-30
We reveal that the four well known vertebrate families of KAT enzymes (GNAT, MYST, P300/CBP, Basal transcription factor/nuclear receptor co-activator) seem to be conserved (Karmodiya et al., 2014; Roth et al., 2001; Sheikh & Akhtar, 2018) in the mangrove rivulus, together with Camello, a potential n
-
It is well known that histamine
2022-03-30
It is well known that histamine functions not only as an inflammation mediator but also as an aminergic neurotransmitter or neuromodulator. Histaminergic neurons [27], [28] and histamine receptor subtypes (H1R [29] and H3R [30]) are widely existed in mammalian central olfactory system. Histamine reg
-
The newest histamine receptor to be discovered
2022-03-30
The newest histamine receptor to be discovered is the H4 receptor, which was identified in humans and cloned in 2000 (Thurmond, 2010). Genetically, the H4 receptor is closely related to the H3 receptor, but is restricted to Penciclovir Sodium synthesis within the spleen, intestines and thymus, and
-
Different crystal structures of both
2022-03-30
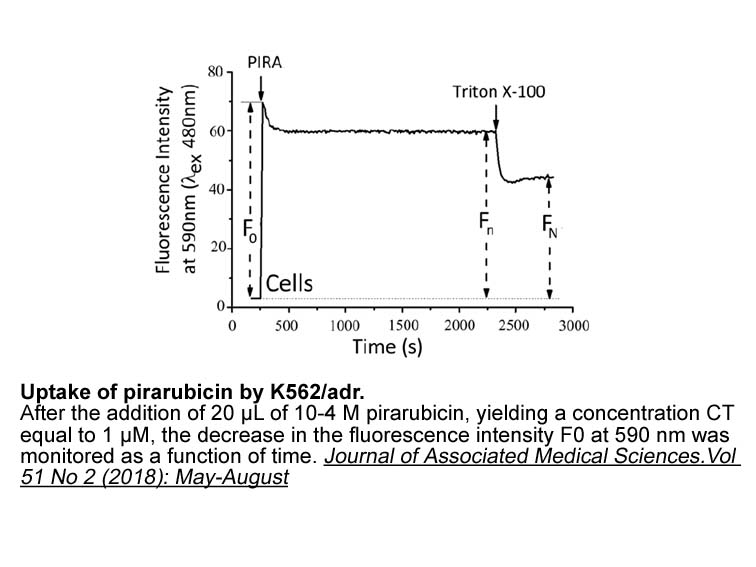
Different crystal structures of both HOs were reported and showed that the three-dimensional structures of proteins (HO-1: PDB code 1N45, HO-2: PDB code 2QPP) are predominantly in an α-helical conformation, with the heme packed between two helices (distal and proximal), and present a remarkable stru
-
Cux is a cell cycle dependent transcription
2022-03-30
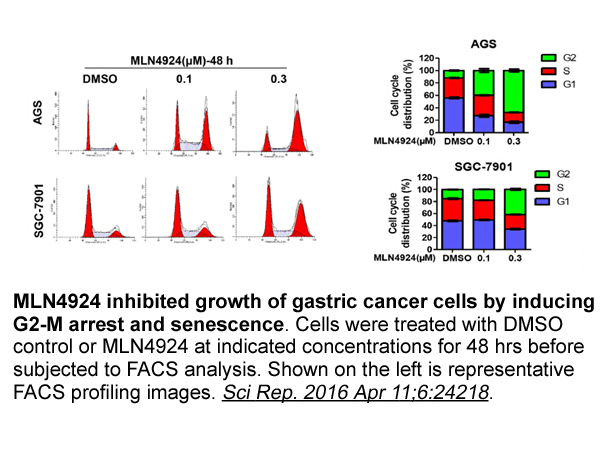
Cux1 is a tazemetostat dependent transcription repressor that is aberrantly expressed in the Pkd1 null, Pkd1CD, and cpk mouse models of PKD, as well as in human ADPKD cells (Vanden Heuvel et al., 1996; Sharma et al., 2005; Paul et al., 2011; Alcalay et al., 2008). In Pkd1 null mice and in human ADP
-
br Conclusion The addition of cellulose
2022-03-30
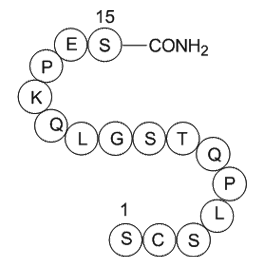
Conclusion The addition of 2-Deoxycytidine to natural substrate increases the number of H-bonds which indicates an increase in the stability of the docking systems. The investigated compounds are more stable than natural substrate in docking systems, where the natural substrate has two H-bonds w
-
Mathematical models play an important role
2022-03-30

Mathematical models play an important role in understanding and predicting the dynamic process of HBV infection. In the 1990s, Nowak et al. proposed a basic model to analyze the effect of antiviral treatment on reducing viral loads (Nowak et al., 1996). Since then, many different mathematical model
-
Glutathione transferases GST have been discovered in many ti
2022-03-29

Glutathione transferases (GST) have been discovered in many tissues including the cornea of humans and several other mammals (Awasthi et al., 1980, Bilgihan et al., 2003; Gondhowiardjo and van Haeringen, 1993; Saneto et al., 1982, Sastry et al., 1995, Singh et al., 1985, Watkins et al., 1991). To da
-
Several studies have shown that the
2022-03-29
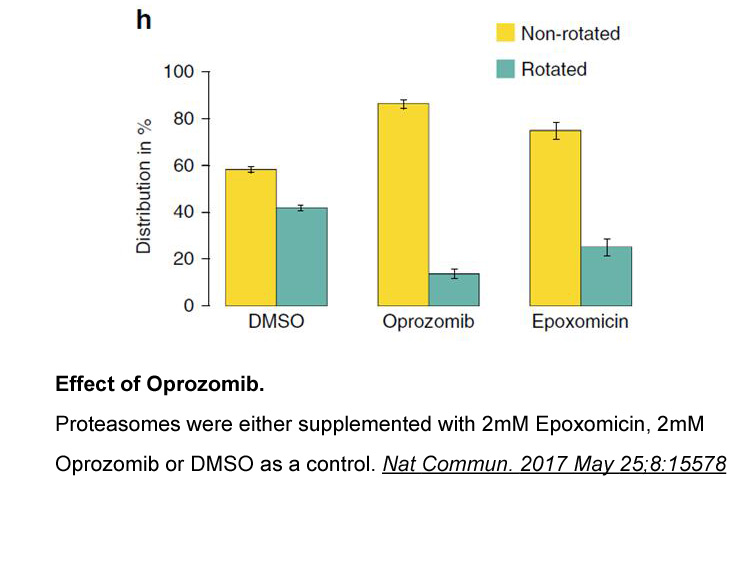
Several studies have shown that the levels of reactive dicarbonyls are higher in patients with diabetes as a result of hyperglycemia.49, 50, 51 Consequently, reactive dicarbonyl-derived AGEs are elevated in plasma and accumulate in tissues prone to secondary complications, including the lens, retin
-
Glial cells have emerged as important protagonists
2022-03-29
Glial cells have emerged as important protagonists of the central nervous system (CNS) physiology (Chen and Swanson, 2003; Kettenmann and Verkhratsky, 2008; Parpura and Verkhratsky, 2012). As widely described in the literature, astrocytes regulate glutamatergic synapses by clearance of glutamate in
14545 records 460/970 page Previous Next First page 上5页 456457458459460 下5页 Last page