Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2018-07
-
If the unwanted objects detected
2019-11-18
If the unwanted objects detected by OpenComet are manually deleted, and then the DNA (%) in tail is computed, the performance of the present method can be compared more effectively. Therefore, performance of OpenComet is analysed in two ways as Approach 1 and Approach 2. Approach 1, considers the D
-
To examine the influence of aromatic motifs on
2019-11-18
To examine the influence of aromatic motifs on the bridging lysine esters we analysed DNA alkylating activity of the set of compounds 1–6. The lysine derivatives were chosen as it is relatively easy to prepare different esters and thereby study the impact of different groups on the reactivity toward
-
NPC L NPC Niemann Pick C like like
2019-11-16
NPC1L1 (NPC1 [Niemann-Pick C-like-1]-like intracellular cholesterol transporter) is the rate-limiting transmembrane transporter for cholesterol N6-Methyl-ATP from the intestinal lumen, and it mediates the absorption of both dietary and biliary cholesterol., , NPC1L1 is the target of the cholestero
-
br Results br Discussion Analysis
2019-11-16
Results Discussion Analysis of EBI2 expression showed that EBI2 is highly expressed in central memory CD8+ T cells that is in line with previous data from human T cells in which these Roflumilast express higher levels of EBI2 than naive or effector memory CD8+ T cells (Hannedouche et al., 201
-
Our data indicate that the ability of these
2019-11-16
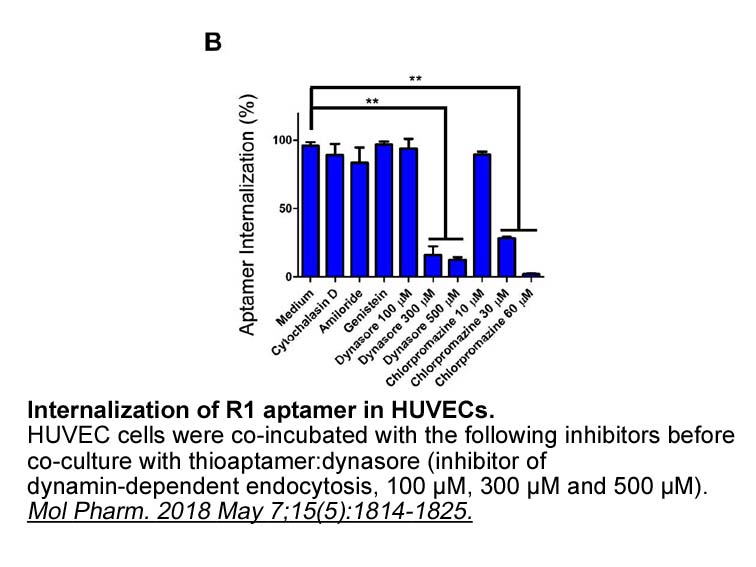
Our data indicate that the ability of these promiscuous kinases to bind chemically diverse inhibitors is defined by the hydrophobic pocket formed by the activation loop, which is only accessible in the DFG-Asp-out conformation. Inhibitors do not artificially induce the DFG-Asp-out conformation as wa
-
DGK is also involved in cell differentiation Previously
2019-11-16
DGKδ is also involved in cell differentiation. Previously, to investigate the physiological roles of DGKδ, DGKδ-deficient mice have been generated. On the basis of the analysis of DGKδ-deficient mice, Crotty et al. reported that DGKδ regulates the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway by a
-
ApicomplexansApicomplexans are unicellular and spore forming
2019-11-16
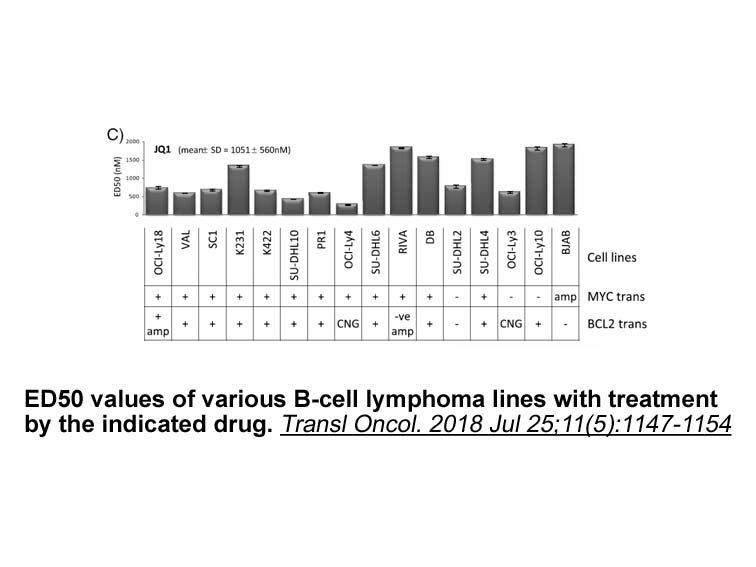
ApicomplexansApicomplexans are unicellular and spore-forming obligate intracellular parasites that occupy diverse host niches (Mogi and Kita 2010). They have remodeled mitochondrial carbon and energy metabolism through reductive evolution. The development of novel drugs is now a very serious challen
-
br Acknowledgements br Membrane bound proton translocating i
2019-11-16
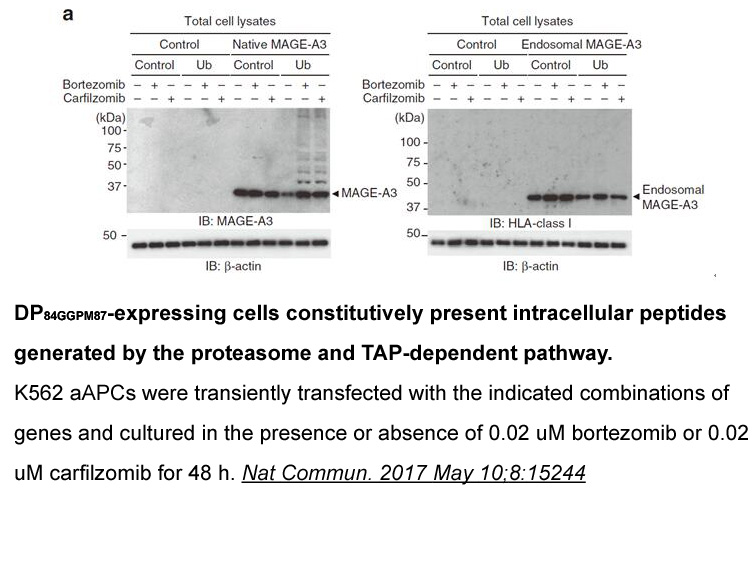
Acknowledgements Membrane-bound proton-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatases (H-PPase; EC 3.6.1.1) belong to a recently identified category of proton pumps, distinct from F-, P-, and V-ATPases, which utilize pyrophosphate hydrolysis as the driving force for H movement across biological membr
-
In the PTEN loss mouse model deletion of ATG gene
2019-11-16
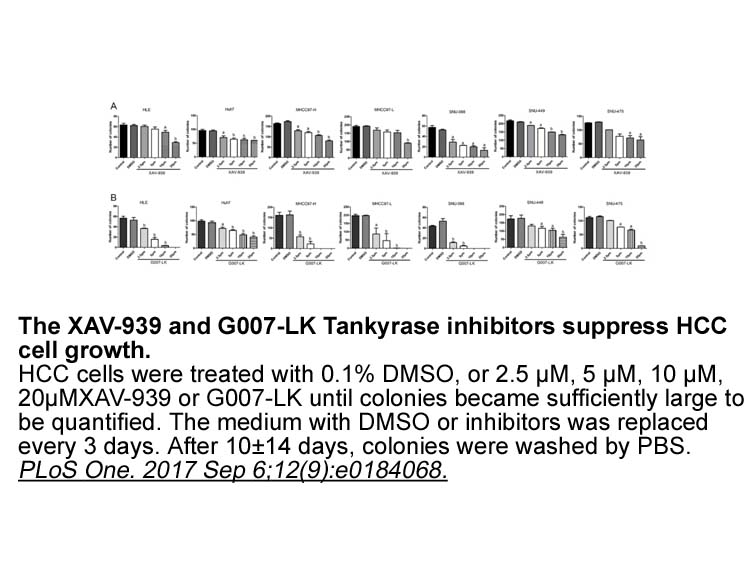
In the PTEN loss mouse model, deletion of ATG7 gene not only caused an autophagy-deficient phenotype, but also postponed the progression of inoculated prostate tumor [22]. On the basis of these experimental facts, these ATG7 and PTEN related genes were then compared with the 3020 BCR-associated gene
-
As described above when EGCG
2019-11-16
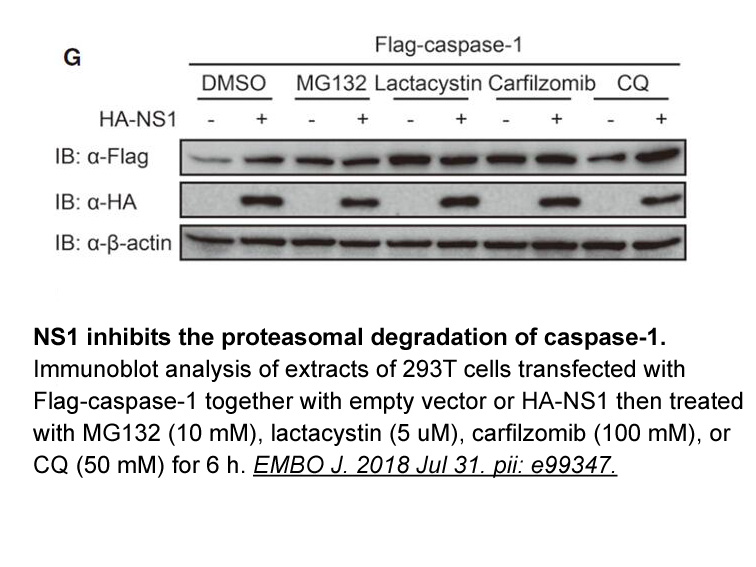
As described above, when EGCG was orally administered, CYP3A expression in the liver decreased; however, the CYP3A expression level in the intestine was unchanged (Fig. 3). Although we remain speculative, one reason for this may be that because the level of intestinal bacteria in the upper part of t
-
bazedoxifene receptor For in vitro expression analysis of CX
2019-11-16
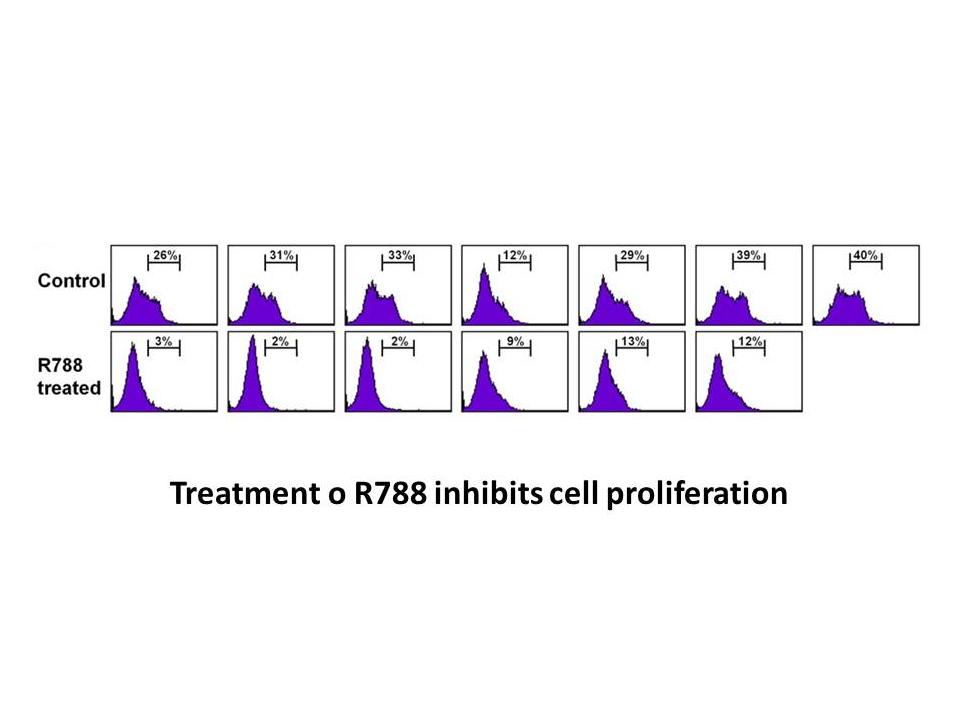
For in vitro expression analysis of CXCL8 and CXCRs by stimulated leucocytes, peripheral blood leucocytes (PBLs) were isolated using Percoll density gradient centrifugation as described earlier . Cell suspensions were adjusted to 5×10/ml. Four milliliters of tissue culture medium were plated per wel
-
Taken together our results demonstrate
2019-11-16
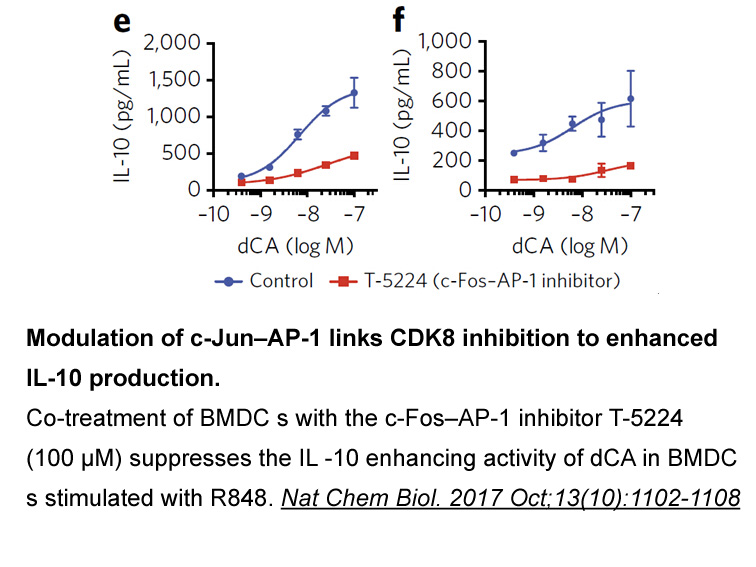
Taken together, our results demonstrate that the changes of striatal dopamine release and locomotor activity observed following chronic nicotine treatment and consequent acute withdrawal are mediated by CRF1, but not CRF2. Previous studies have already indicated that blocking CRF1 would prevent some
-
Introduction Robust evidence suggests that genetic factors
2019-11-16
Introduction Robust evidence suggests that genetic factors influence an individual\'s susceptibility to BD (Craddock and Sklar, 2013). Yet, no single, high penetrance gene has been identified with direct causality (Craddock and Sklar, 2009). The largest GWAS to date for identifying genes conferring
-
The heterogeneity among studies that investigated the
2019-11-16
The heterogeneity among studies that investigated the association of COMT Val158Met with alexithymia was also significant (Ham et al., 2005; Min et al., 2016; Swart et al., 2011; Zekioglu et al., 2014). The healthy status, drug effect, and other demographic variables also influenced one\'s ability o
-
As the primary model we selected LDL receptor knockout mice
2019-11-16

As the primary model we selected LDL-receptor knockout mice because these resemble the human plasma lipoprotein profile more closely. Currently, genetic models with reduced milk cholesterol content, which mimic cholesterol-free formula feeding, are unavailable. Thus, instead of modifying milk choles
14534 records 929/969 page Previous Next First page 上5页 926927928929930 下5页 Last page